1. What is loan analysis
Loan analysis is an evaluation process that identifies if loans are made on feasible terms and if borrowers are able to pay back the loan. This process analyses the eligibility of the potential borrower, in other words, creditworthiness of borrower, against the criteria set for lending. Mainly, as it aids in assessing the skills and financial knowledge of the borrower to determine the level of risk involved.
2. Why proper evaluation is required
Lending facilities are the largest and most obvious source of credit risk the banks and non-banking financial institutions. The main source of income for banks is the difference between the interest rate charged by borrowers and what is paid to depositors. Therefore, after keeping a portion of deposits as reserves banks lend to people who demand money as lending facilities and bank charges interest from them.
3. Steps in loan process
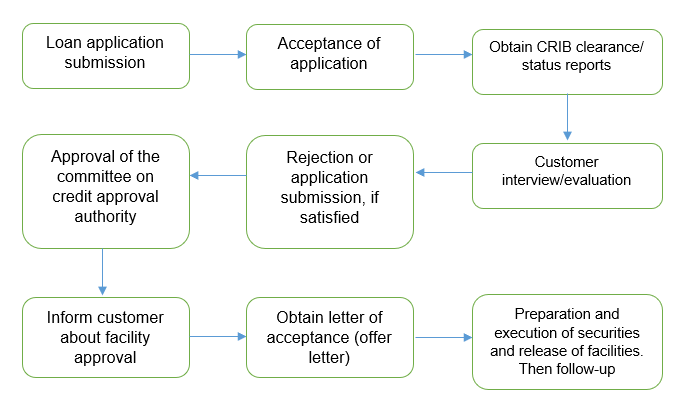
4. Common lapses in loan proposals
Common lapses in the loan proposals are as follows,
- Submission of insufficient documents – not mentioning statutory payment records in cash flow documents, etc.
- Insufficient collateral guarantee – Guarantors of borrower are not strong against the facility they seek for.
- Failing to mention cash in-flow records, repayment structure
- Realizability of collateral provided – Already leased property as a collateral (have to move out the tenant)
- Irregularities in Borrower’s records with same institute or with other banks, such as unsatisfactory repayment history and lapses in current account records etc.
- Issues with the provided security for the loan which to be assigned to the bank. Sometimes security is not insured or cannot be insured. Also, it may have mortgaged to any other entity as well.
- Approvals of certain authorities are not taken – RDA, Environmental, Aviation, etc.
5. Lending principles and best practices
The financial institutions should follow below lending principles and best practices before granting any facility.
- Safety – critically evaluation the borrower’s capacity to repay the borrowed amount with the interest attached – creditworthiness of the borrower
- Liquidity – when depositors request for withdrawals bank should maintain healthy liquidity level
- Spread – should try to minimize concertation risk by diversified into many sectors, industries or fields
- Profitability – financial institutions have to charge interest rate based on the risk attach with the facility to generate profit
- Purpose – lending for approved purposes (not for any illegal or gambling)
- End use – banker should ensure that the money lent has been used for the said purpose
- Viability based lending – determine the viability of the business to check the repayment of borrower
- Need based finance – real requirement of the customer
- Own stake – borrower’s contributions towards the transaction/business
- National priorities – check whether it a national priority. eg: agriculture, tourism, SME.
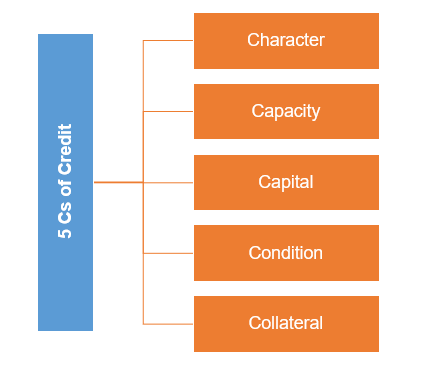
6. Lending policies, procedures and evaluation
7. Credit culture
Credit culture is the unique combination of policies, practices, experience, and management attitudes that defines the lending environment and determines the lending behaviour acceptable to the financial institution. The four C’s, namely, Communication, Consistency, Competency and Collaboration lay the foundation to make a strong credit culture in the organization. An ideal banking culture is cultivated when every person knows what the objectives and goals of the bank is.
